B.3 Using GNU Radio and USRP
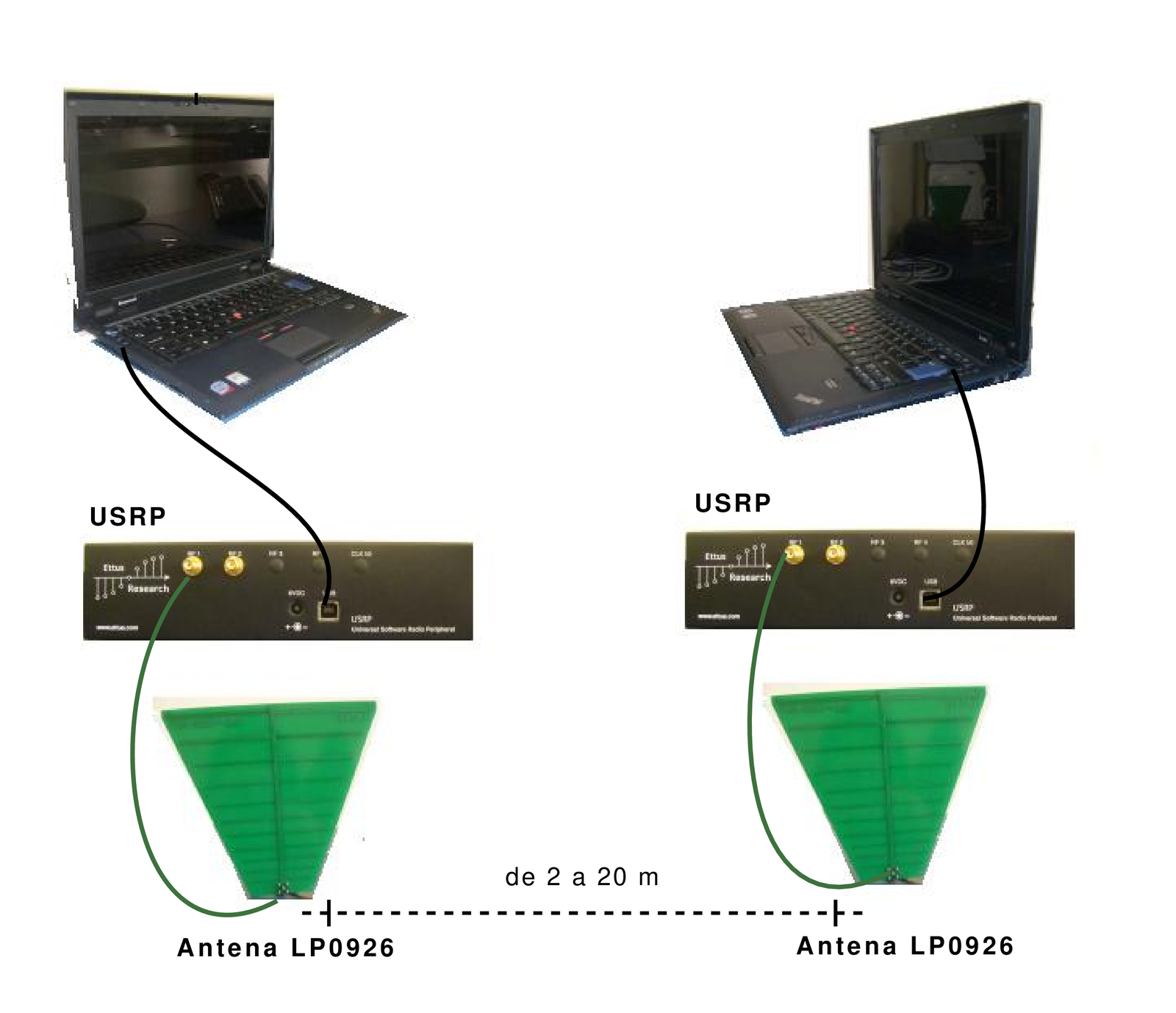
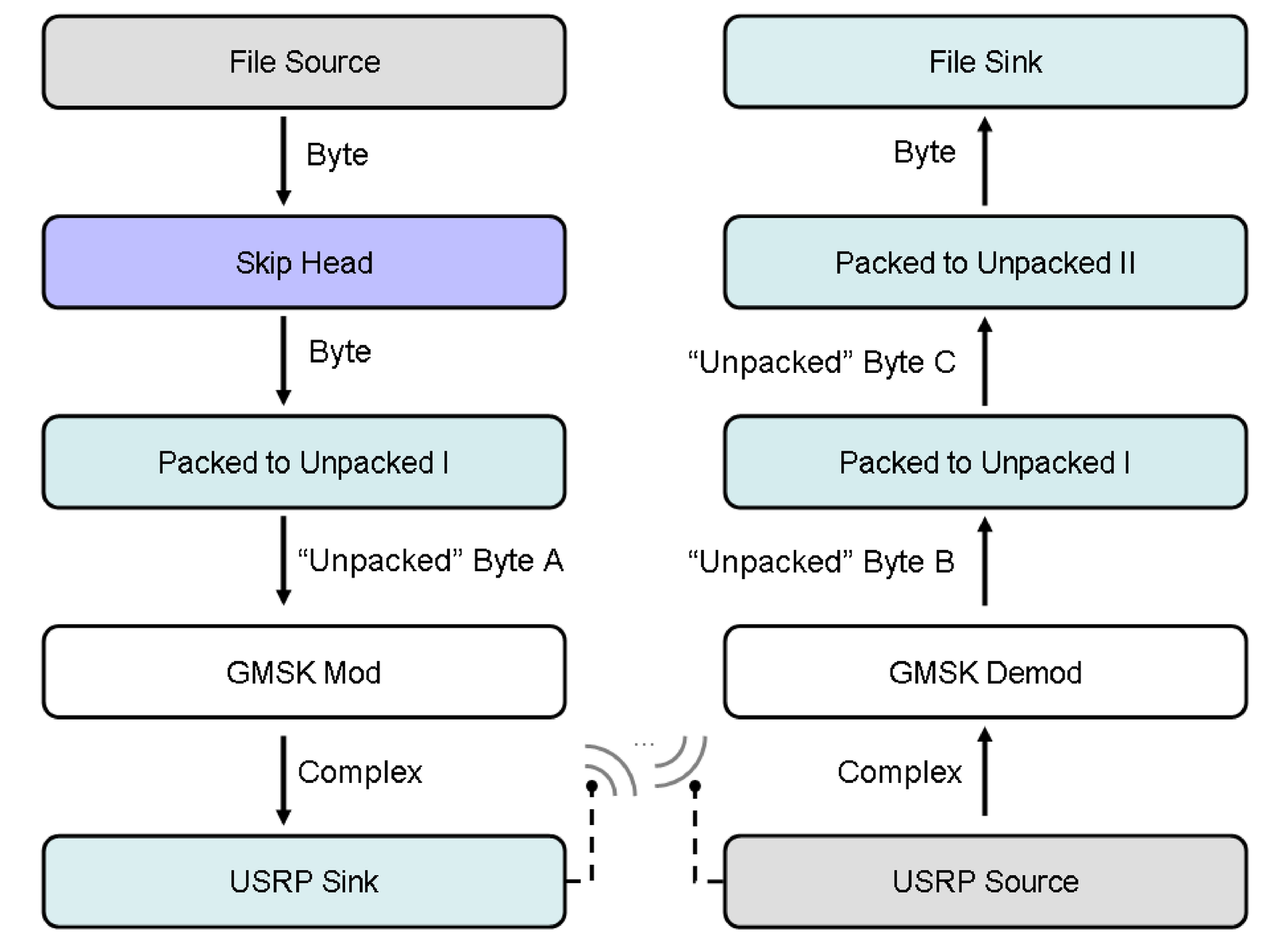
An experiment is described here to illustrate. Two USRP mother boards were used, each one connected to a FLEX 2400 daughter board, which work in the frequency range from 2.4 to 2.5 GHz. The goal is to transmit a given file (for example, a figure in the BMP format) using the GMSK modulation with a carrier frequency of 2.5 GHz. The second USRP receives the signal, demodulates, writes to disk and compares with the original file. The data flow graph depicted in Figure B.3 lists the processing blocks, as well as their corresponding output. Figure B.4 provides a illustration of the involved equipment. The first transmitter block reads the file, while its successor block ignores the first bytes (file header) and passes the remaining bytes to an “unpacker”, which converts bytes into right-justified bits in each output byte. The GMSK modulator then sends complex symbols to the USRP, which converts them into a modulated signal. The inverse process takes place at the receiver. The extra Packed to Unpacked block is necessary due to the format adopted by the demodulator.